二叉树的三种遍历方式
Table of Contents
概述
- 二叉树(Binary tree)是树形结构的一个重要类型。
- 许多实际问题抽象出来的数据结构往往是二叉树形式,即使是一般的树也能简单地转换为二叉树,而且二叉树的存储结构及其算法都较为简单,因此二叉树显得特别重要。
- 二叉树特点是每个节点最多只能有两棵子树,且有左右之分。
- 二叉树是n个有限元素的集合,该集合或者为空、或者由一个称为根(root)的元素及两个不相交的、被分别称为左子树和右子树的二叉树组成,是有序树。
- 当集合为空时,称该二叉树为空二叉树。在二叉树中,一个元素也称作一个节点。
二叉树的三种遍历顺序
- 前序遍历: 根结点 -> 左子树 -> 右子树
- 中序遍历: 左子树 -> 根结点 -> 右子树
- 后序遍历: 左子树 -> 右子树 -> 根结点
例子
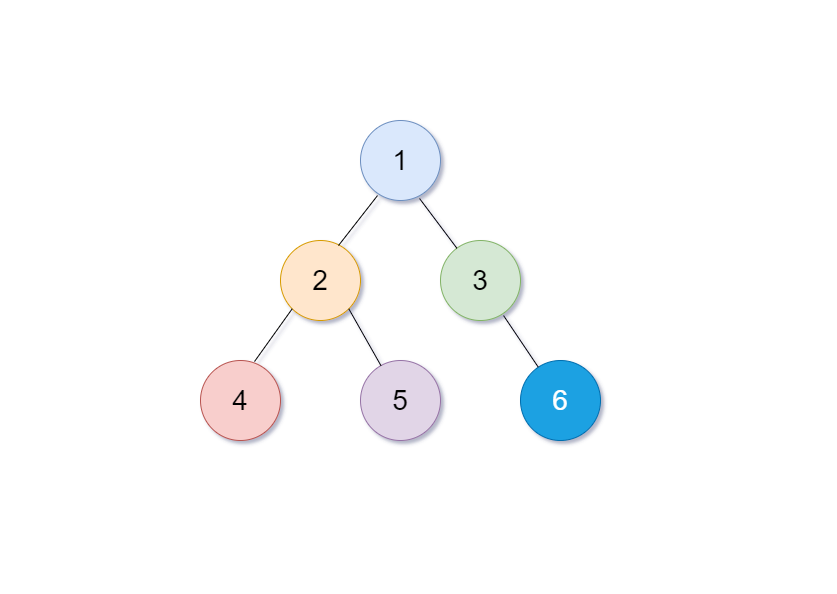
BinaryTreeTraversalDemo.java
package com.leetcode.editor.tree;
import com.leetcode.utils.TreeNode;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 二叉树遍历
*/
public class BinaryTreeTraversalDemo {
/**
* 前序
*/
public static List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
preorder(root, res);
return res;
}
public static void preorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
// 前序遍历,根->左->右的顺序
// 把当前节点的值添加到集合
res.add(root.val);
// 递归遍历左子树,直到没有左子树
preorder(root.left, res);
// 递归遍历右子树,直到没有右子树
preorder(root.right, res);
}
/**
* 中序
*/
public static List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
inorder(root, res);
return res;
}
public static void inorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null) {
// 递归结束条件,空则返回
return;
}
// 中序遍历,左->根->右的顺序
// 递归遍历左子树,直到没有左子树
inorder(root.left, res);
// 把当前节点的值添加到集合
res.add(root.val);
// 递归遍历右子树,直到没有右子树
inorder(root.right, res);
}
/**
* 后序
*/
public static List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
postorder(root, res);
return res;
}
public static void postorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
// 后序遍历,左->右->根的顺序
// 递归遍历左子树,直到没有左子树
postorder(root.left, res);
// 递归遍历右子树,直到没有右子树
postorder(root.right, res);
// 把当前节点的值添加到集合
res.add(root.val);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeNode treeNode = TreeNode.simpleTree();
TreeNode.show(treeNode);
System.out.println("\n前序");
preorderTraversal(treeNode).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("\n中序");
inorderTraversal(treeNode).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("\n后序");
postorderTraversal(treeNode).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
输出:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ \
4 5 6
前序
1
2
4
5
3
6
中序
4
2
5
1
3
6
后序
4
5
2
6
3
1
TreeNode.java
package com.leetcode.utils;
/**
* 树
*
* @author loquy
* @date 2021 /12/06 10:21
*/
public class TreeNode {
/**
* The Val.
*/
public int val;
/**
* The Left.
*/
public TreeNode left;
/**
* The Right.
*/
public TreeNode right;
/**
* Instantiates a new Tree node.
*/
public TreeNode() {
}
/**
* Instantiates a new Tree node.
*
* @param val the val
*/
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
/**
* Instantiates a new Tree node.
*
* @param val the val
* @param left the left
* @param right the right
*/
public TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
/**
* Gets tree depth.
*
* @param root the root
* @return the tree depth
*/
public static int getTreeDepth(TreeNode root) {
return root == null ? 0 : (1 + Math.max(getTreeDepth(root.left), getTreeDepth(root.right)));
}
/**
* Write Array
* @param currNode
* @param rowIndex
* @param columnIndex
* @param res
* @param treeDepth
* @return void
*/
private static void writeArray(TreeNode currNode, int rowIndex, int columnIndex, String[][] res, int treeDepth) {
// 保证输入的树不为空
if (currNode == null) {
return;
}
// 先将当前节点保存到二维数组中
res[rowIndex][columnIndex] = String.valueOf(currNode.val);
// 计算当前位于树的第几层
int currLevel = ((rowIndex + 1) / 2);
// 若到了最后一层,则返回
if (currLevel == treeDepth) {
return;
}
// 计算当前行到下一行,每个元素之间的间隔(下一行的列索引与当前元素的列索引之间的间隔)
int gap = treeDepth - currLevel - 1;
// 对左儿子进行判断,若有左儿子,则记录相应的"/"与左儿子的值
if (currNode.left != null) {
res[rowIndex + 1][columnIndex - gap] = "/";
writeArray(currNode.left, rowIndex + 2, columnIndex - gap * 2, res, treeDepth);
}
// 对右儿子进行判断,若有右儿子,则记录相应的"\"与右儿子的值
if (currNode.right != null) {
res[rowIndex + 1][columnIndex + gap] = "\\";
writeArray(currNode.right, rowIndex + 2, columnIndex + gap * 2, res, treeDepth);
}
}
/**
* Show.
*
* @param root the root
*/
public static void show(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
System.out.println("EMPTY!");
}
// 得到树的深度
int treeDepth = getTreeDepth(root);
// 最后一行的宽度为2的(n - 1)次方乘3,再加1
// 作为整个二维数组的宽度
int arrayHeight = treeDepth * 2 - 1;
int arrayWidth = (2 << (treeDepth - 2)) * 3 + 1;
// 用一个字符串数组来存储每个位置应显示的元素
String[][] res = new String[arrayHeight][arrayWidth];
// 对数组进行初始化,默认为一个空格
for (int i = 0; i < arrayHeight; i ++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arrayWidth; j ++) {
res[i][j] = " ";
}
}
// 从根节点开始,递归处理整个树
// res[0][(arrayWidth + 1)/ 2] = (char)(root.val + '0');
writeArray(root, 0, arrayWidth/ 2, res, treeDepth);
// 此时,已经将所有需要显示的元素储存到了二维数组中,将其拼接并打印即可
for (String[] line: res) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < line.length; i ++) {
sb.append(line[i]);
if (line[i].length() > 1 && i <= line.length - 1) {
i += line[i].length() > 4 ? 2: line[i].length() - 1;
}
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
/**
*
* 1
* / \
* 2 3
* / \ \
* 4 5 6
*
*/
public static TreeNode simpleTree(){
TreeNode left2 = new TreeNode(4);
TreeNode right2 = new TreeNode(5);
TreeNode left = new TreeNode(2, left2, right2);
TreeNode right3 = new TreeNode(6);
TreeNode right = new TreeNode(3, null, right3);
return new TreeNode(1, left, right);
}
}